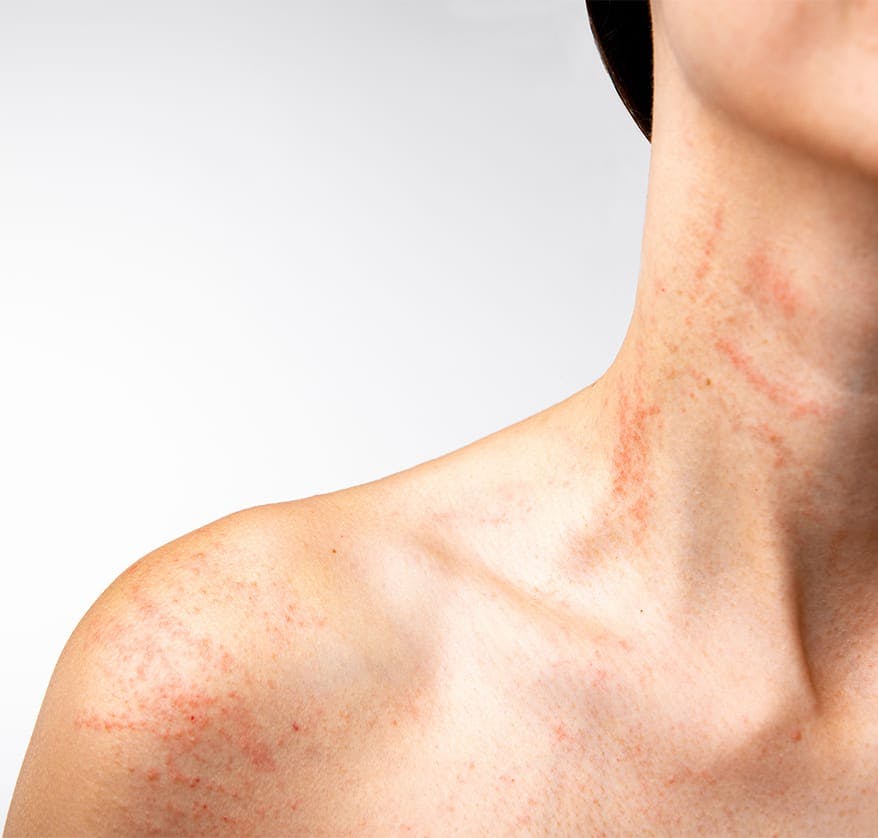
Causes of Hives
Hives are caused when the body releases the chemical histamine. Histamine is a compound that the body releases in response to inflammation, infection, or acute stress. When histamine is released, the blood vessels under the skin, called capillaries, are dilated. This dilation results in the appearance of hives.
Often times, the exact cause of why a person has hives is unknown. Usually, histamine is released in response to an allergic reaction; allergies are one of the most common causes of hives.
Other causes of hives may include:
- Infections
- Excessive scratching
- Anxiety
- Sun exposure
- Extreme temperatures
- Pressure or rubbing on the skin