Your Family Deserves the Best Care Book an Appointment
Your skin health matters, so don’t delay. Our clinicians look forward to treating you and your family at one of our local New England practices.
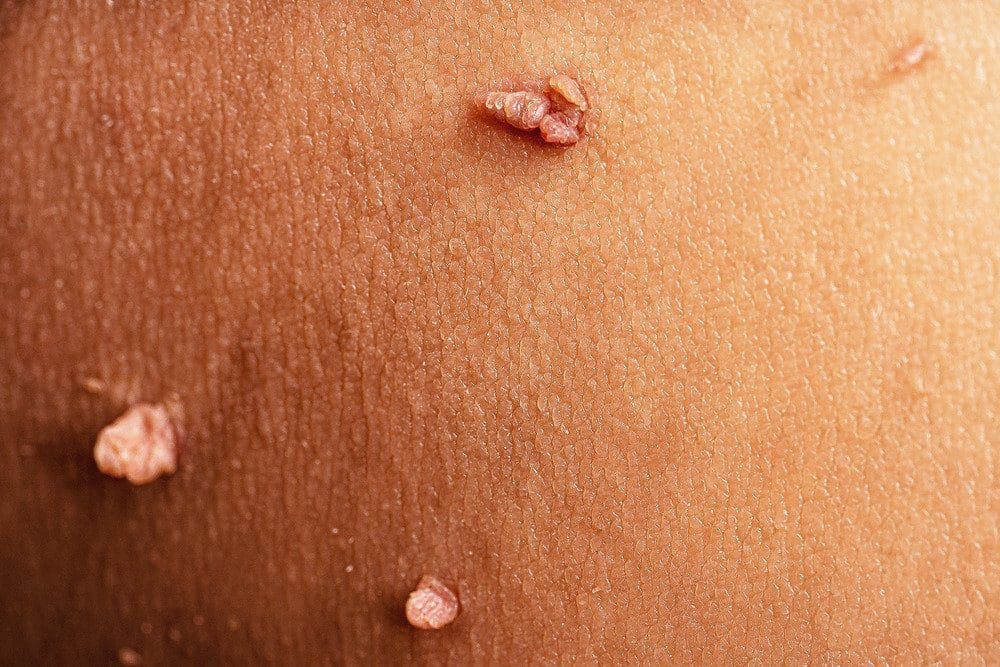
Find Your Nearest APDerm CenterGenital warts, also known as condyloma acuminata, are a type of noncancerous skin growth caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Genital warts typically appear in the genital and anal regions and can also affect the mucous membranes.
Their name derives from the presence of small, raised growths, which are caused by HPV and can have a rough, bumpy texture. They can also vary in size and can be quite painful or uncomfortable, especially when pressure is applied during various activities such as sexual intercourse.
Genital warts are different from other warts, such as common warts, due to their unique characteristics and specific locations. While common warts typically appear on areas like the hands and fingers, for example, genital warts are exclusively found in the genital and anal regions. Additionally, unlike other warts, genital warts tend to grow on moist and delicate mucous membranes, making them highly sensitive and more likely to induce discomfort, pain, or itching sensations. Genital warts are highly contagious and can easily spread from person to person or from one part of the body to another.
HPV is mainly transmitted through direct contact, entering the body through tiny skin abrasions or openings in the skin or mucous membrane. This is why genital warts are often transmitted through sexual contact. If left untreated, genital warts can persist for an extended period, resulting in discomfort and distress.
Therefore, as with any other warts, it is imperative to seek appropriate treatment for genital warts and take preventive measures to effectively manage this condition.
Symptoms of genital warts can vary significantly from one person to another, and it’s possible that some individuals may not exhibit any discernible symptoms, which can increase the risk of transmission. When symptoms of genital warts do occur, they typically include the following:
Genital warts often appear as small, flesh-colored, or pink growths that develop in or around the genital and anal regions. These growths are frequently elevated and may have a surface that resembles cauliflower, but they can take on various forms, contributing to their distinct appearance.
Some individuals affected by these warts may experience persistent itching or discomfort in the affected area. This discomfort can range from mild irritation to more pronounced itching and often results from the presence of genital warts, making the affected region sensitive and uncomfortable.
Genital warts can occasionally lead to bleeding, especially during sexual intercourse or when subjected to friction or irritation. The fragile nature of wart tissue can make it susceptible to bleeding when disturbed, and this symptom can be a cause for concern for individuals dealing with this condition.
In certain instances, genital warts may cause pain, particularly if they are large or situated in areas prone to friction, such as during movement or sexual activity. The presence of these warts can result in localized discomfort, making daily activities or sexual encounters painful and uncomfortable.
The presence of warts in areas with natural moisture can lead to excess wetness and dampness. This heightened moisture can intensify the discomfort experienced by individuals with genital warts, contributing to a constant sense of dampness, which can be uncomfortable.
Although relatively rare, genital warts located near the urethral opening or within the vaginal canal may occasionally result in discomfort during urination. This discomfort can arise when the warts interfere with the normal flow of urine or cause localized irritation, leading to unease during urination.
Symptoms related to genital warts can differ significantly from person to person, and not everyone affected will experience all of these symptoms. If you suspect you have warts near your genitals or have concerns about your sexual health, consult a healthcare professional. Practicing safe sex and considering HPV vaccination can also aid in reducing the risk of contracting genital warts and associated complications.


Genital warts, known medically as condyloma acuminata, are mainly caused by infection with specific strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV types 6 and 11 are the primary causes, typically found in genital and anal areas where the virus can thrive. In this instance, HPV is transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex, and it enters the skin or mucous membranes through tiny cuts, abrasions, or skin openings. Factors that increase the risk of these warts include engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners, having contact with individuals with multiple sexual partners, and a weakened immune system. However, not everyone exposed to HPV develops genital warts, as the virus can remain dormant or be cleared by the immune system. Practicing safe sex, HPV vaccination, and regular sexually transmitted infection (STI) testing are recommended to reduce the risk of genital warts and related complications.
It is vital to remember that genital warts are highly contagious, and the likelihood of infection varies from person to person. Therefore, to minimize the risk of HPV transmission and subsequent development of genital warts, it is advisable to practice safe sex, use barrier methods like condoms, and consider HPV vaccination. Additionally, maintaining good sexual hygiene is essential in reducing the risk of these warts.
Diagnosing genital warts typically begins with a visual examination conducted by a healthcare professional. During this examination, the healthcare provider focuses on the genital and anal areas, which are the common sites where genital warts appear. They carefully assess the appearance, texture, and precise location of the warts, all while noting any accompanying symptoms like pain, discomfort, itching, or burning.
Recognizing the unique characteristics of genital warts is a key aspect of the diagnosis process. These warts usually present as raised, bumpy growths with a cauliflower-like appearance. By carefully observing these distinctive features, healthcare providers can confidently identify genital warts. The healthcare provider may also inquire about the individual’s medical history, including any prior experiences with genital warts, HPV infection, or other sexually transmitted infections.
In some instances, a dermatoscope (i.e. a handheld device with magnification and lighting capabilities) may be used by a healthcare professional to closely examine the warts. This technique, known as dermatoscopy, can provide a more detailed assessment of the wart’s features, including any characteristic black dots. If any uncertainty remains in the diagnosis, the healthcare provider may recommend a skin biopsy. During a skin biopsy, a small sample of the wart is extracted and sent for further analysis under a microscope. This can help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential skin conditions.
It is important to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis of genital warts, as healthcare professionals are trained to differentiate them from other skin conditions. They are also best suited to recommend suitable treatment options based on the diagnosis. If you suspect you have genital warts or require assistance in exploring treatment options, we highly recommend you consult a healthcare professional.

The treatment of genital warts serves the goals of wart removal, symptom relief, and prevention of recurrence. Various treatment options exist, and the selection depends on factors such as wart size, location, and quantity, as well as individual preferences and healthcare provider recommendations.
For mild cases of genital warts, over-the-counter (OTC) topical treatments containing ingredients like imiquimod or podofilox are often employed. These agents either engage the body’s immune system to combat the virus or directly target the warts. In instances of more extensive or persistent warts, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger topical medications with heightened concentrations of active ingredients, like podophyllin or podofilox, or recommend more potent creams.
Cryotherapy offers an alternative genital wart treatment, involving the application of liquid nitrogen to the warts, leading to blistering and eventual detachment. Typically administered by healthcare professionals, this process may necessitate multiple sessions. Electrocautery provides another avenue, utilizing an electrical current to burn off the warts, often performed in a healthcare setting with local anesthesia.
Laser therapy, conducted by dermatologists, employs a focused laser beam to target and obliterate the blood vessels that supply the warts, causing gradual shrinkage and disappearance. Surgical removal is an option for large or stubborn genital warts, involving excision, where the warts are surgically removed using a scalpel or scissors under local or general anesthesia.
In some cases, healthcare providers may propose immunotherapy, where a substance is applied to the warts to stimulate the body’s immune system to combat the virus and warts. It’s crucial to recognize that while these treatments eliminate visible warts, they do not cure the underlying HPV infection, which might still be present in the body, potentially leading to wart recurrence. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are typically required to monitor and manage the condition.
To reduce the risk of HPV transmission and recurrence, safe sex practices like condom use can be effective, alongside HPV vaccination to safeguard against certain HPV strains, including those responsible for these type of warts. Ultimately, consultation with a healthcare provider is significant for determining the most suitable treatment approach for individual cases of these warts.

Preventing these warts involves a combination of safe practices and vaccination. Here are the key measures for genital warts prevention:
Engaging in safe sex is pivotal in reducing the risk of contracting warts near your genitals. This involves consistent and correct use of latex or polyurethane condoms during sexual activity. Condoms act as a physical barrier, reducing skin-to-skin contact, which can help minimize the transmission of HPV. However, condoms do not offer complete protection because HPV can infect areas not covered by the condom, such as the genital and anal regions. Therefore, while condoms are a valuable preventive tool, they are not foolproof.
Undergoing HPV vaccination is a highly effective strategy for preventing genital warts. HPV vaccines provide immunity against various high-risk HPV strains, including those accountable for genital warts. Typically recommended for adolescents and young adults, particularly before becoming sexually active, these vaccines can also be beneficial for older individuals. By bolstering the body’s defenses against these HPV strains, vaccination significantly reduces the risk of developing genital warts and HPV-related complications.
Routine visits to a healthcare provider are instrumental in the early detection and management of genital warts. During these appointments, healthcare professionals can conduct examinations, discuss sexual health practices, and offer guidance on HPV vaccination. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment and potentially prevent the spread of the virus to others. Additionally, healthcare providers can address any concerns or questions about HPV and its associated risks.
Maintaining proper sexual hygiene is a fundamental aspect of preventing these warts. Adequate washing and cleaning of the genital and anal areas, for example, are essential for reducing the risk of HPV transmission. By maintaining cleanliness in these regions, individuals can minimize the chances of the virus gaining a foothold and causing infection. Good sexual hygiene complements other preventive measures, such as regular sexual health check-ups, to create a strong defense against genital warts.
Discussing sexual history, HPV vaccination, and safe sex practices empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health, fosters trust, and ensures both parties actively engage in preventing HPV and other sexually transmitted infections. Reducing the number of sexual partners is also effective in lowering the risk of HPV exposure. Fewer partners mean a lower likelihood of encountering the virus, enhancing prevention efforts and promoting sexual health.
Remember that no preventive measure is foolproof, and there is always a degree of risk associated with sexual activity. However, by adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of contracting genital related warts and HPV-related complications. Consulting with a healthcare provider to discuss vaccination and sexual health is an important step in these warts prevention.

It is crucial to seek medical assistance if you detect visible warts in the genital or anal areas, and if you encounter symptoms like pain, discomfort, itching, bleeding, or signs of infection. Equally significant is addressing the situation if you observe the warts multiplying or growing in size. Finally, when the diagnosis is uncertain or if over-the-counter treatments prove ineffective, it is also advisable to seek professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your sexual health, including the risk of contracting or transmitting genital warts and other sexually transmitted infections, discussing these concerns with a healthcare provider is essential. They can offer guidance on preventive measures, such as HPV vaccination and safe sex practices. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are vital, particularly if you are sexually active or considering HPV vaccination, as these visits play a crucial role in the early detection and effective treatment of genital warts, reducing transmission risk and ensuring you receive proper care.


Your skin health matters, so don’t delay. Our clinicians look forward to treating you and your family at one of our local New England practices.
Find Your Nearest APDerm CenterWe use cookies and other tools to enhance your experience on our website and to analyze our website traffic. For more information about these cookies and the data collected, please refer to our Privacy Policy.